कार्बन
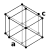
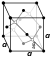
 Graphite (left) and diamond (right), two allotropes of carbon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| आम लच्छन (जनरल प्रापर्टी) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| एलोट्रोप | graphite, diamond | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| रूपरंग | graphite: black diamond: clear | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| स्टैंडर्ड परमाणु वजन (Ar, standard) | [12.0096, 12.0116] conventional: 12.011 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| पीरियाडिक टेबल में Carbon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| परमाणु नंबर (Z) | 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ग्रुप | group 14 (carbon group) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| पीरियड | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ब्लॉक | p | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| इलेक्ट्रान कन्फिगरेशन | [He] 2s2 2p2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Electrons per shell | 2, 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| भौतिक लच्छन | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| फेज at STP | solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| सब्लिमेशन ताप | 3915 K (3642 °C, 6588 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| घनत्व (लगभग रू.टे.) | amorphous: 1.8–2.1 g/cm3[1] graphite: 2.267 g/cm3 diamond: 3.515 g/cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ट्रिपल प्वाइंट | 4600 K, 10,800 kPa[2][3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| फ्यूजन के एन्थाल्पी | graphite: 117 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| मोलर हीट कैपसिटी | graphite: 8.517 J/(mol·K) diamond: 6.155 J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| परमाणु संबंधी लच्छन | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ऑक्सीडेशन स्टेट | −4, −3, −2, −1, 0, +1,[4] +2, +3,[5] +4[6] (a mildly acidic oxide) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| इलेक्ट्रोनिगेटिविटी | Pauling scale: 2.55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| आयनाइजेशन एनर्जी |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| कोवैलेंट रेडियस | sp3: 77 pm sp2: 73 pm sp: 69 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| वान डर वाल्स रेडियस | 170 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| अन्य लच्छन | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| क्रिस्टल स्ट्रक्चर | graphite: simple hexagonal (black) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| क्रिस्टल स्ट्रक्चर | face-centered diamond-cubic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound thin rod | diamond: 18,350 m/s (at 20 °C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| थर्मल ऍक्सपैंशन | diamond: 0.8 µm/(m·K) (at 25 °C)[7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| थर्मल कंडक्टिविटी | graphite: 119–165 W/(m·K) diamond: 900–2300 W/(m·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| इलेक्ट्रिकल रेजिस्टिविटी | graphite: 7.837 µΩ·m[8] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| चुंबकी क्रम | diamagnetic[9] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| यंग्स माड्युलस | diamond: 1050 GPa[7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| शियर माड्युलस | diamond: 478 GPa[7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| बल्क माड्युलस | diamond: 442 GPa[7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| पोइसंस रेशियो | diamond: 0.1[7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| मोहो हार्डनेस | graphite: 1–2 diamond: 10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| सीएएस (CAS) नंबर | 7440-44-0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| इतिहास | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| खोज | Egyptians and Sumerians[10] (3750 BCE) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recognized as an element by | Antoine Lavoisier[11] (1789) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| carbon के प्रमुख आइसोटोप | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
कार्बन (अंग्रेजी: कॉर्बन; Carbon, मूल लैटिन: carbo "कोइला" से अंग्रेजी में आइल शब्द) एगो रासायनिक तत्व हवे जेकर चीन्हा C (रोमन कैपिटल अच्छर "सी") हवे आ परमाणु नंबर 6 हवे। ई गैर-धातु हवे आ टेट्रावैलेंट—मने कि कोवेलेंट बंध बनावे खातिर चार इलेक्ट्रान के उपलब्धता वाला हऽ। ई पीरियोडिक टेबल में ग्रुप 14 में रखल जाला।[17] कार्बन के तीन गो आइसोटोप प्राकृतिक रूप से मिले लें, 12C आ 13C स्टेबल होलें, जबकि 14C एगो रेडियोन्यूकलाइड हवे, एकरे क्षय के हाफ-लाइफ लगभग 5,730 साल होला।[18] कार्बन कुछ अइसन तत्व सभ में से एक बा जेकरे बारे में बहुत प्राचीन जमाना से लोगन के मालुम बाटे।[19]
कार्बन पृथ्वी पर बहुत सारे रूपों में पाया जाता है| जैसे - हिरा, ग्रेफाइट, फुलरिन आदि|लेकिन हिरा कार्बन का शुद्धतम रूप है जो की बहुत कठोर होता है इससे काच पत्थर आदि काटे जा सकते है| दुसरि तरफ ग्रेफाइट बहुत नर्म और कोमल होता है,इसका उपयोग लिखने वाली पेन्सिल में किया जाता है.....Read More
संदर्भ
[संपादन करीं]- ↑ Lide, D. R., ed. (2005). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (86th ed.). Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0486-5.
- ↑ Haaland, D (1976). "Graphite-liquid-vapor triple point pressure and the density of liquid carbon". Carbon. 14 (6): 357. doi:10.1016/0008-6223(76)90010-5.
- ↑ Savvatimskiy, A (2005). "Measurements of the melting point of graphite and the properties of liquid carbon (a review for 1963–2003)". Carbon. 43 (6): 1115. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2004.12.027.
- ↑ "Fourier Transform Spectroscopy of the Electronic Transition of the Jet-Cooled CCI Free Radical" (PDF). Retrieved 2007-12-06.
- ↑ "Fourier Transform Spectroscopy of the System of CP" (PDF). Retrieved 2007-12-06.
- ↑ "Carbon: Binary compounds". Retrieved 2007-12-06.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 Properties of diamond, Ioffe Institute Database
- ↑ https://www.nde-ed.org/GeneralResources/MaterialProperties/ET/ET_matlprop_Misc_Matls.htm
- ↑ Magnetic susceptibility of the elements and inorganic compounds, in Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 81st edition, CRC press.
- ↑ "History of Carbon and Carbon Materials - Center for Applied Energy Research - University of Kentucky". Caer.uky.edu. Retrieved 2008-09-12.
- ↑ Senese, Fred (2000-09-09). "Who discovered carbon?". Frostburg State University. Retrieved 2007-11-24.
- ↑ Conventional Atomic Weights 2013. Commission on Isotopic Abundances and Atomic Weights
- ↑ Standard Atomic Weights 2013. Commission on Isotopic Abundances and Atomic Weights
- ↑ "Fourier Transform Spectroscopy of the System of CP" (PDF). Retrieved 2007-12-06.
- ↑ "Fourier Transform Spectroscopy of the Electronic Transition of the Jet-Cooled CCI Free Radical" (PDF). Retrieved 2007-12-06.
- ↑ "Carbon: Binary compounds". Retrieved 2007-12-06.
- ↑ "carbon | Facts, Uses, & Properties". Encyclopedia Britannica (अंग्रेजी में). Archived from the original on 2017-10-24.
- ↑ "Carbon – Naturally occurring isotopes". WebElements Periodic Table. Archived from the original on 2008-09-08. Retrieved 2008-10-09.
- ↑ "History of Carbon". Archived from the original on 2012-11-01. Retrieved 2013-01-10.